Step 5: Navigation Full Stack#
Introduction to the Navigation Full Stack#
The Edge Insights for Autonomous Mobile Robots navigation full stack contains a lot of components that help the robot navigate, avoid obstacles, and map an area. For example:
Intel® RealSense™ camera node: receives input from the camera and publishes topics used by the vSLAM algorithm
Robot base node: receives input from the motor controller (for example, from wheel encoders) and sends commands to the motor controller to move the robot
ros-base-camera-tf: Usesstatic_transform_publisherto create transforms betweenbase_linkandcamera_linkstatic_transform_publisherpublishes a static coordinate transform to tf using an x/y/z offset in meters and yaw/pitch/roll in radians. The period, in milliseconds, specifies how often to send a transform.yaw = rotation on the x axis
pitch = rotation on the y axis
roll = rotation on the z axis
collab-slam: A Collaborative Visual SLAM Framework for Service Robots paperFastMapping: an algorithm to create a 3D voxelmap of a robot’s surroundings, based on Intel® RealSense™ camera’s depth sensor data and provide the 2D map needed by the Navigation 2 stack
nav2: the navigation packageWandering: demonstrates the combination of middleware, algorithms, and the ROS 2 navigation stack to move a robot around a room without hitting obstacles
In Edge Insights for Autonomous Mobile Robots, there two examples:
cd $CONTAINER_BASE_PATH
ls 01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/05_tutorials/aaeon_wandering__aaeon_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2.tutorial.yml
ls 01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/05_tutorials/pengo_wandering__kobuki_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2.tutorial.yml
One is for AAEON’s UP Xtreme i11 Robotic Kit, and the other is for Cogniteam’s Pengo robot.
Create a Parameter File for Your Robotic Kit#
To create a parameter file for your robotic kit:
cp 01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/05_tutorials/aaeon_wandering__aaeon_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2.tutorial.yml 01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/05_tutorials/generic_robot_wandering__aaeon_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2.tutorial.yml
# Replace generic_robot_nav to a name that makes sense to your robotic kit.
gedit 01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/05_tutorials/generic_robot_wandering__aaeon_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2.tutorial.yml
# you can also use any other preferred editor, it is important though to keep the path.
Make all of the changes that are specific to your robotic kit:
Replace the
aaeon-amr-interfacetarget with the generic robot node you created in Step 3: Robot Base Node ROS 2 Node.Remove the
ros-base-teleoptarget because this is specific to AAEON’s UP Xtreme i11 Robotic Kit.In the ROS 2 command file, change the Navigation 2 target so that
params_filetargets the parameter file you created in Step 4: Robot Base Node ROS 2 Navigation Parameter File.from:
params_file:=${CONTAINER_BASE_PATH}/01_docker_sdk_env/artifacts/01_amr/amr_generic/param/aaeon_nav.param.yamlto:
params_file:=${CONTAINER_BASE_PATH}/01_docker_sdk_env/artifacts/01_amr/amr_generic/param/generic_robot_nav.param.yamlIn the
ros-base-camera-tftarget, change the transform values fromstatic_transform_publisher. The values for x, y, and z depend on where your Intel® RealSense™ camera is set.
Start Mapping an Area with Your Robot#
Place the robot in an area with multiple objects in it.
Check that EI for AMR environment is set:
echo $AMR_TUTORIALS # should output the path to EI for AMR tutorials /home/user/edge_insights_for_amr/Edge_Insights_for_Autonomous_Mobile_Robots_2023.1/AMR_containers/01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/05_tutorials
If nothing is output, refer to Get Started Guide for Robots Step 5 for information on how to configure the environment.
Start mapping the area:
docker compose -f $AMR_TUTORIALS/generic_robot_wandering__aaeon_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2.tutorial.yml up
Expected result: The robot starts wandering around the room and mapping the entire area.
On a different terminal, prepare the environment to visualize the mapping and the robot using rviz2.
Note
If available, use a different development machine because rviz2 consumes a lot of resources that may interfere with the robot.
# If using a different machine, set the same ROS_DOMAIN_ID as on the robot #export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=42 docker compose -f $AMR_TUTORIALS/rviz_robot_wandering.yml up
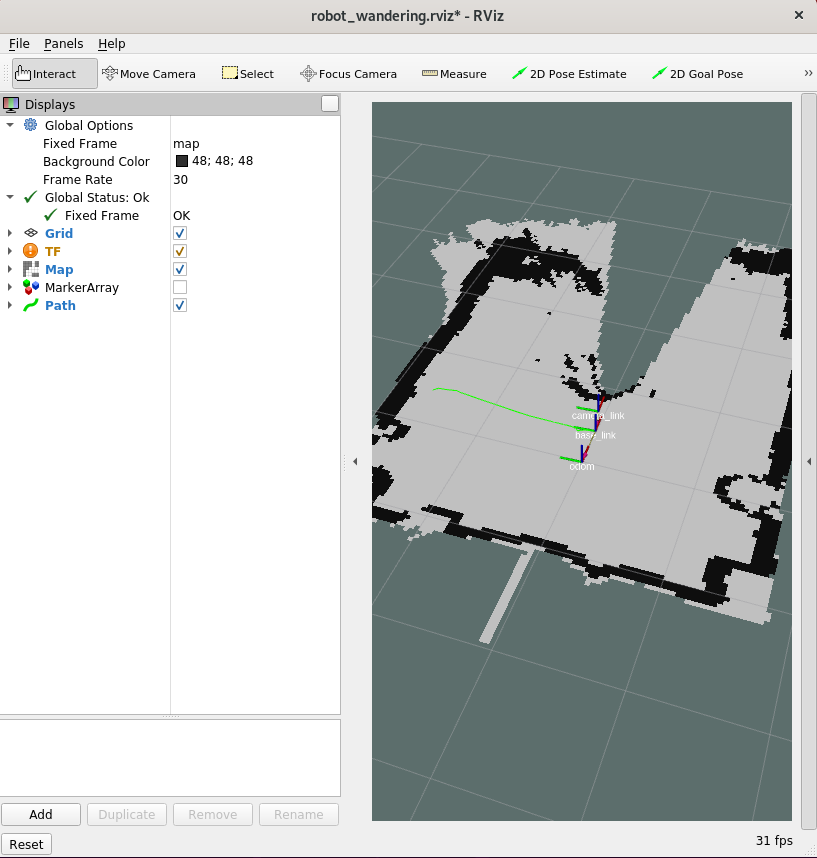
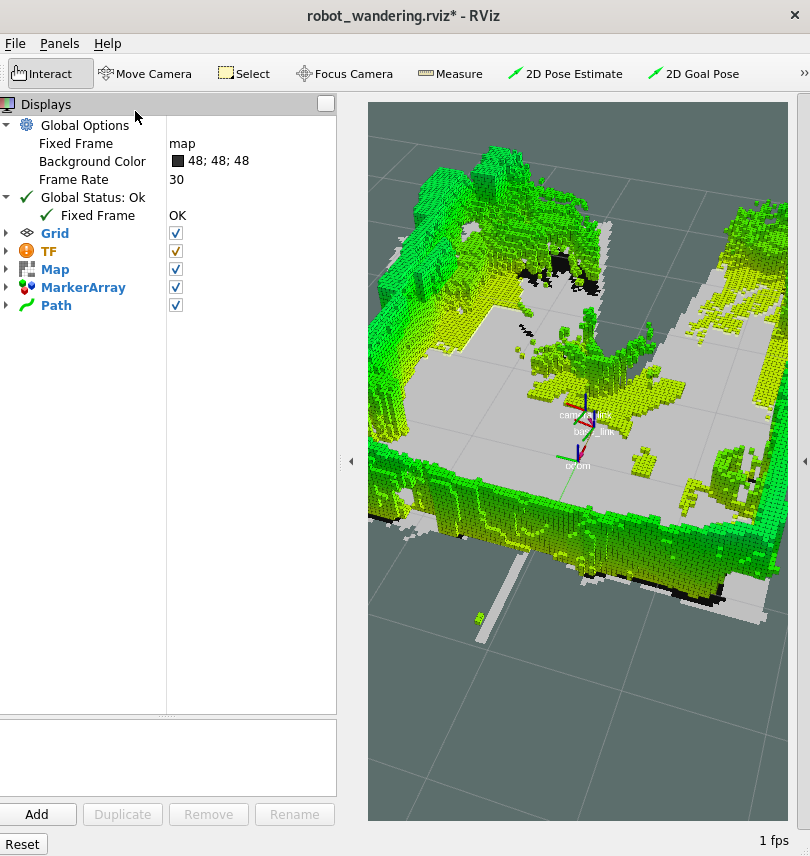
To see the map in 3D, check the MarkerArray:
Note
Displaying in 3D consumes a lot of system resources. Intel® recommends opening rviz2 on a development system. The development system needs to be in the same network and have the same ROS_DOMAIN_ID set.
To stop the robot from mapping the area, do the following:
Type
Ctrl-cin the terminal where the aaeon_wandering__aaeon_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2_ukf.tutorial.yml was run.Use
docker compose downto remove the containers:
docker compose -f $AMR_TUTORIALS/generic_robot_wandering__aaeon_realsense_collab_slam_fm_nav2.tutorial.yml down --remove-orphans