Intel® Edge Software Device Qualification (Intel® ESDQ) for EI for AMR#
Overview#
Intel® Edge Software Device Qualification (Intel® ESDQ) for EI for AMR provides customers with the capability to run an Intel® provided test suite at the target system, with the goal of enabling partners to determine their platform’s compatibility with the EI for AMR.
The target of this self certification suite is the EI for AMR compute systems. These platforms are the brain of the Robot Kit. They are responsible to get input from sensors, analyze them, and give instructions to the motors and wheels to move the EI for AMR.
How It Works#
The EI for AMR Test Modules interacts with the Intel® ESDQ CLI through a common test module interface (TMI) layer which is part of the Intel® ESDQ binary. Intel® ESDQ generates a complete test report in HTML format, along with detailed logs packaged as one zip file, which you can manually choose to email to: Edge.Software.Partners@intel.com
Note
Each test and its pass/fail criteria is described below. To jump to the installation process, go to Download and Install Intel® ESDQ for EI for AMR.
Intel® ESDQ for EI for AMR contains the following test modules.
Docker* Container
This module verifies that the EI for AMR comes as a Docker* container and it can run on the target platform.
For more information, go to the Docker* website.
The test is considered Pass if:
The Docker* container can be opened.
Intel® RealSense™ Camera
This module verifies the capabilities of the Intel® RealSense™ technology on the target platform.
For more information, go to the Intel® RealSense™ website.
The tests within this module verify that the following features are installed properly on the target platform and that EI for AMR and the Intel® RealSense™ camera are functioning properly:
The camera is detected and is working.
Intel® RealSense™ SDK.
The tests are considered Pass if:
The Intel® RealSense™ SDK 2.0 libraries are present in Docker* container.
A simple C++ file can be compiled using g++ and -lrealsense2 flag.
Intel® RealSense™ Topics are listed and published.
The number of FPS (Frames Per Second) are as expected.
Intel® VTune™ Profiler
This module runs the Intel® VTune™ Profiler on the target system.
For more information, go to the Intel® VTune™ Profiler website.
The test is considered Pass if:
VTune™ Profiler runs without errors.
VTune™ Profiler collects Platform information.
rviz2 and FastMapping
This module runs the FastMapping application (the version of octomap optimized for Intel®) on the target system and uses rviz2 to verify that it works as expected.
For more information, go to the rviz wiki.
The test is considered Pass if:
FastMapping is able to create a map out of a pre-recorded ROS 2 bag.
Turtlesim
This module runs the Turtlesim ROS2 application on the target system and checks if it works as expected.
For more information, go to the Turtlesim wiki.
The test is considered Pass if:
Turtlesim opens and runs without error.
Intel® oneAPI Base Toolkit
This module verifies some basic capabilities of Intel® oneAPI Base Toolkit on the target platform.
For more information, go to the Intel® oneAPI Base Toolkit website.
The tests within this module verify that the following features are functioning properly on the target platform:
DPC++ compiler
CUDA to DPC++ converter
This test is considered Pass if:
A simple C++ file can be compiled using the DPC++ compiled and it runs as expected.
CUDA can be installed.
A CUDA specific file can be converted to DPC++ and it runs as expected.
OpenVINO™ Toolkit
This module verifies two core features of the OpenVINO™ Toolkit:
OpenVINO™ model optimizer
Object detection using TensorFlow*
The test is considered Pass if:
The OpenVINO™ model optimizer is capable to transform a TensorFlow model to an Intermediate Representation (IR) of the network, which can be inferred with the Inference Engine.
Object Detection on CPU
This module verifies object detection using OpenVINO™ on CPU.
The test is considered Pass if:
The object is detected.
If the test is failed, you can check the expected picture and the actual picture obtained by the test.
Object Detection on GPU
This module verifies object detection using OpenVINO™ on GPU.
The test is considered Pass if:
The object is detected.
If the test is failed, you can check the expected picture and the actual picture obtained by the test.
GStreamer* Video
This module verifies if a GStreamer* Video Pipeline using GStreamer* Plugins runs on the target system.
The test is considered Pass if:
The Video Pipeline was opened on the host without errors.
GStreamer* Audio
This module verifies if a GStreamer* Audio Pipeline using GStreamer* Plugins runs on the target system.
The test is considered Pass if:
The Audio Pipeline was opened on the host without errors.
GStreamer* Autovideosink Plugin - Display
This module verifies if a stream from a camera compatible with libv4l2 can be opened and displayed using GStreamer*.
The test is considered Pass if:
No Error messages are displayed while running the gst-launch command.
This test may FAIL, or it may be skipped if the target system does not have a Web Camera connected.
GStreamer* Intel® RealSense™ Video Plugin
This module verifies if a GStreamer* Video Pipeline using the Intel® RealSense™ Plugin runs on the target system.
The test is considered Pass if:
No Error messages are displayed while running the gst-launch command.
This test may FAIL, or it may be skipped if the target system does not have a Intel® RealSense™ Camera connected.
ADBSCAN
This module verifies if the ADBSCAN algorithm works on the target system.
The test is considered Pass if:
The ADBSCAN algorithm works on the target system.
Collaborative Visual SLAM
This module verifies if the collaborative visual SLAM algorithm works on the target system.
The test is considered Pass if:
The collaborative visual SLAM algorithm works on the target system.
Kudan visual SLAM
This module verifies if the Kudan visual SLAM algorithm works on the target system.
The test is considered Pass if:
The Kudan visual SLAM algorithm works on the target system.
Get Started#
This tutorial takes you through installing the Intel® ESDQ CLI tool, which is installed as part of EI for AMR. Refer to How It Works before starting the installation. To use this tutorial, you must Download and Install Intel® ESDQ for EI for AMR.
Download and Install Intel® ESDQ for EI for AMR#
Intel® ESDQ is optionally bundled with EI for AMR solutions.
Download a configuration that includes Intel® ESDQ.
Go to the Product Download page.
Select Robot Complete Kit.
Select Customize Download.
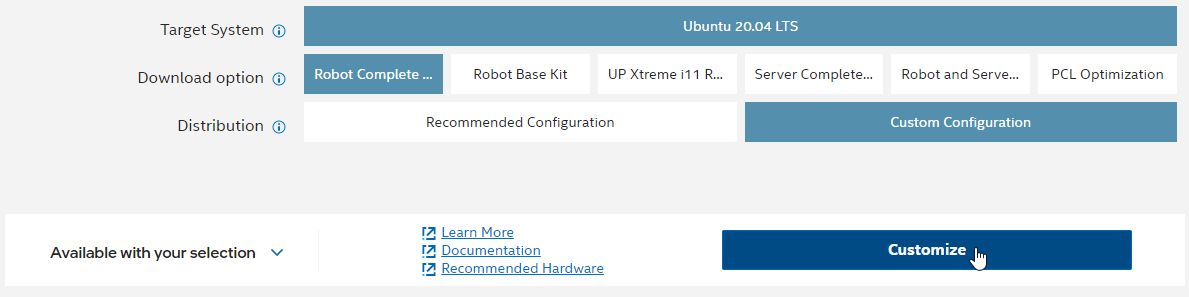
Click Next, until you get to step 4.
On the Intel Tools page, make sure that Intel® Edge Software Device Qualification is checked.

On the Reference Implementations page, make sure that AMR Bag Files and AMR Kudan SLAM are selected:
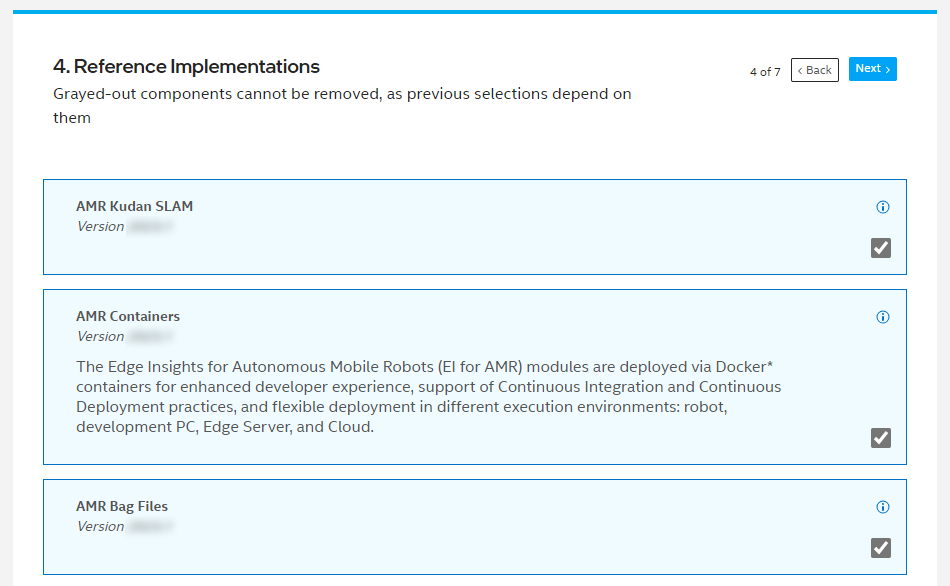
Click Next until you get to the Download page, and click on Download.
Follow the steps in the Get Started Guide for Robots to extract and install EI for AMR.
Run your target self-certification. Intel® ESDQ for EI for AMR contains three types of self-certifications:
Run the Self-Certification Application for Compute Systems for certifying Intel® based compute systems with the EI for AMR software
Run the Self-Certification Application for RGB Cameras for certifying RGB cameras with the EI for AMR software
Run the Self-Certification Application for Depth Cameras for certifying depth cameras with the EI for AMR software
Run the Self-Certification Application for Compute Systems#
Change the directory:
cd $HOME/edge_software_device_qualification/Edge_Software_Device_Qualification_For_AMR_*/esdq
Unzip the ROS 2 bags used in the tests:
unzip ../AMR_containers/01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/06_bags.zip -d ../AMR_containers/01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/ sudo chmod 0777 -R ../AMR_containers/01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/06_bags
Run the Intel® ESDQ test, and generate the report:
export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=19 ./esdq run -r
Expected output (These results are for illustration purposes only.)
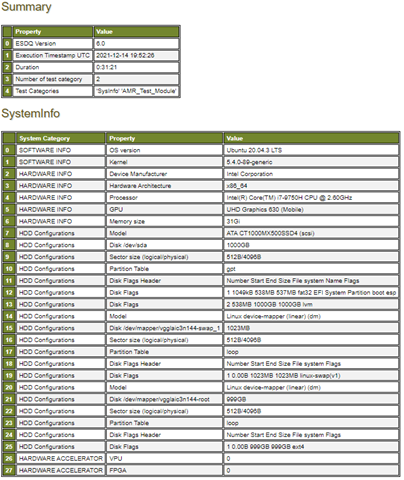
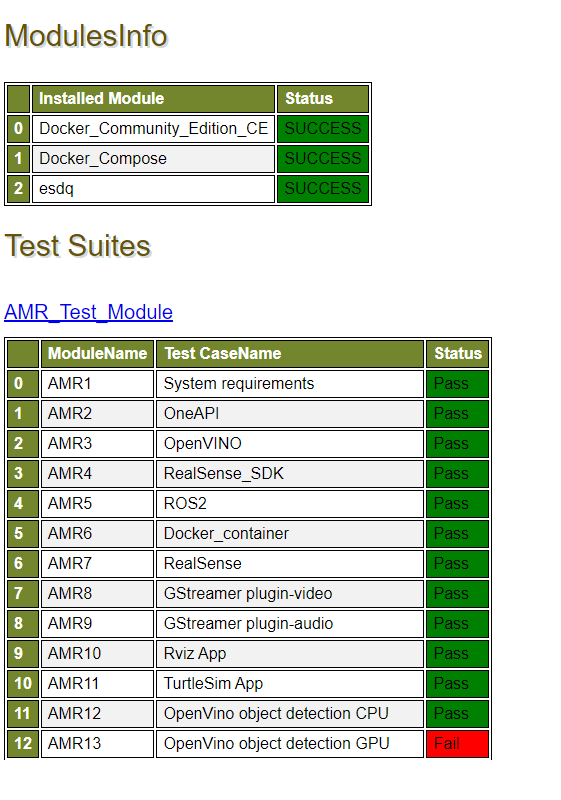
Note
The OpenVINO™ Object Detection GPU Test Failure above is shown for demonstration purposes only. The test is expected to pass.
Run the Self-Certification Application for RGB Cameras#
Prerequisites: The RGB camera has a ROS 2 node that can publish:
The RGB raw image on topic: “/camera/color/image_raw” on fixed frame: “camera_color_frame”
Note
The following steps use the Intel® RealSense™ ROS 2 node as an example. You must change the node to your actual camera ROS 2 node.
Change the directory:
cd $HOME/edge_software_device_qualification/Edge_Software_Device_Qualification_For_AMR_*/esdq
Start the the sensor ROS 2 node:
Replace the commands with the commands you use to open up the RGB camera for the certification Docker* container. If there is no Docker* container, run the RGB camera node in a ROS 2 environment after setting the ROS_DOMAIN_ID.
source ./01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/common/docker_compose.source export CONTAINER_BASE_PATH=`pwd` docker compose -f 01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/01_amr/amr-sdk.all.yml run realsense bash
Replace the commands with the commands you use to open up the RGB camera for the certification ROS 2 node.
source ros_entrypoint.sh # set a unique id here that is used in all terminals export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=19 ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py &
The self-certification test expects the camera stream to be on the “/camera/color/image_raw” topic. This topic must be visible in rviz2 using the “camera_color_frame” fixed frame. If your camera ROS 2 node does not stream to that topic by default, use ROS 2 remapping to publish to that topic.
ros2 topic list
Run the Intel® ESDQ test, and generate the report:
export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=19 ./esdq run -r -p "sensors_rgb"
Run the Self-Certification Application for Depth Cameras#
Prerequisites: The depth camera has a ROS 2 node that can publish:
Point cloud points on topic: “/camera/depth/color/points” on the fixed frame: “camera_link”
The depth raw image on topic: “/camera/depth/image_rect_raw” on the fixed frame: “camera_link”
Note
The following steps use the Intel® RealSense™ ROS 2 node as an example. You must change the node to your actual camera ROS 2 node.
Change the directory:
cd $HOME/edge_software_device_qualification/Edge_Software_Device_Qualification_For_AMR_*/esdq
Start the the sensor ROS 2 node:
Replace the commands with the commands you use to open up the depth camera for the certification Docker* container. If there is no Docker* container, run the depth camera node in a ROS 2 environment after setting the ROS_DOMAIN_ID.
source ./01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/common/docker_compose.source export CONTAINER_BASE_PATH=`pwd` docker compose -f 01_docker_sdk_env/docker_compose/01_amr/amr-sdk.all.yml run realsense bash
Replace the commands with the commands you use to open up the depth camera for the certification ROS 2 node.
source ros_entrypoint.sh # set a unique id here that is used in all terminals export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=19 ros2 launch realsense2_camera rs_launch.py pointcloud.enable:=true &
The self-certification test expects the camera stream to be on the “/camera/depth/color/points” and “/camera/depth/image_rect_raw” topics. These topics must be visible in rviz2 using the “camera_link” fixed frame. If your camera ROS 2 node does not stream to that topic by default, use ROS 2 remapping to publish to that topic.
ros2 topic list
Run the Intel® ESDQ test, and generate the report:
export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=19 ./esdq run -r -p "sensors_depth"
Send Results to Intel®#
Once the automated and manual tests are executed successfully, you can submit your test results and get your devices listed on the Intel® Edge Software Recommended Hardware site.
Send the zip file that is created after running Intel® ESDQ tests to: Edge.Software.Partners@intel.com.
For example, after one of our local runs the following file was generated:
esdqReport_2022-03-09_13:22:28.zip
Troubleshooting#
For issues, go to: Troubleshooting for Robot Tutorials.
Support Forum#
If you’re unable to resolve your issues, contact the Support Forum.