Tutorial to Use GPU ORB Extractor Feature¶
This tutorial shows how to use GPU orb-extractor feature library API.
The GPU orb-extractor feature library offers thread-safe support for both single and multiple cameras.
This tutorial illustrates GPU orb-extractor feature library usage with OpenCV cv::Mat and cv::Keypoints.
It explains employing multiple CPU threads with multiple ORB extractor objects, as well as using a single orb-extractor feature object to handle multiple camera inputs.
The multithread feature provides more flexibility for visual SLAM to call multiple objects of the orb-extractor feature library.
Note
This tutorial can be run both inside and outside a Docker* image. We assume that the liborb-lze-dev Deb package has been installed,
and the user has copied the tutorial directory from /opt/intel/orb_lze/samples/ to a user-writable directory.
Prepare the environment:
main.cppshould be in the directory with following content:1#include "orb_extractor.h" 2#include "cmd_parser.h" 3#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> 4#include <opencv2/features2d.hpp> 5#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> 6#include <fstream> 7#include <chrono> 8#include <memory> 9#include <thread> 10 11using namespace std; 12 13constexpr uint32_t max_num_keypts_ = 2000; 14constexpr int num_levels_ = 8; 15constexpr int ini_fast_thr_ = 20; 16constexpr int min_fast_thr_ = 7; 17constexpr float scale_factor_ = 1.2f; 18 19struct All_Images 20{ 21 std::string image_title; 22 cv::Mat img; 23}; 24 25std::vector<All_Images> gl_images; 26 27inline double getTimeStamp() 28{ 29 std::chrono::system_clock::duration d = std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch(); 30 std::chrono::seconds s = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(d); 31 return s.count() + (std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::microseconds>(d - s).count()) / 1e6; 32} 33 34void extract(int num_cam, const std::string& image_path, const std::string& thread_name, int iterations) 35{ 36 int num_of_cameras = num_cam; 37 std::vector<cv::Mat> all_images; 38 all_images.resize(num_of_cameras); 39 for(int i = 0; i < num_of_cameras; i++) 40 { 41 all_images[i] = cv::imread(image_path, cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE); 42 } 43 44 std::vector<std::vector<KeyType>> keypts(num_of_cameras); 45 std::vector<MatType> all_descriptors(num_of_cameras); 46 47#ifdef OPENCV_FREE 48 Mat2d *images = new Mat2d[num_of_cameras]; 49 std::vector<MatType> in_image_array; 50 for( int i = 0; i < num_of_cameras; i++) 51 { 52 images[i] = Mat2d(all_images[i].rows, all_images[i].cols, all_images[i].data); 53 in_image_array.push_back(images[i]); 54 } 55 std::vector<MatType> in_image_mask_array; 56 std::vector<MatType> descriptor_array; 57#else 58 const cv::_InputArray in_image_array(all_images); 59 const cv::_InputArray in_image_mask_array; 60 const cv::_OutputArray descriptor_array(all_descriptors); 61#endif 62 63 std::vector<std::vector<float>> mask_rect; 64 65 std::string thread_id = thread_name; 66 67 try 68 { 69 auto extractor = std::make_shared<orb_extractor>(max_num_keypts_, scale_factor_, num_levels_, ini_fast_thr_, min_fast_thr_, num_of_cameras, mask_rect); 70 extractor->set_gpu_kernel_path(ORBLZE_KERNEL_PATH_STRING); 71 72 double total_host_time = 0.0; 73 74 for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++) 75 { 76 std::cout << "iteration " << i+1 <<"/" << iterations << "\r"; 77 std::cout.flush(); 78 double host_start = getTimeStamp(); 79 extractor->extract(in_image_array, in_image_mask_array, keypts, descriptor_array); 80 double host_end = getTimeStamp(); 81 double host_time_diff = (host_end - host_start)/(float)iterations; 82 total_host_time += host_time_diff; 83 } 84 85 std::cout << "\n" << thread_id << ": gpu host time=" << total_host_time*1000.0 << std::endl; 86 } 87 catch(const std::exception& e) 88 { 89 std::cout << "\n Exception caught:" << e.what(); 90 exit(1); 91 } 92 std::vector<std::vector<cv::KeyPoint>> all_keypts(num_of_cameras); 93 94#ifdef OPENCV_FREE 95 for(int i=0; i < num_of_cameras; i++) 96 { 97 auto& gpu_keypts = keypts.at(i); 98 for (int pt=0; pt < gpu_keypts.size(); pt++) 99 { 100 all_keypts[i].emplace_back(cv::KeyPoint(gpu_keypts[pt].x, gpu_keypts[pt].y, 101 gpu_keypts[pt].size, gpu_keypts[pt].angle, gpu_keypts[pt].response, 102 gpu_keypts[pt].octave, -1)); 103 } 104 } 105#else 106 for(int i=0; i < num_of_cameras; i++) 107 { 108 all_keypts.at(i) = keypts.at(i); 109 } 110#endif 111 112 std::vector<cv::Mat> out; 113 out.resize(num_of_cameras); 114 115 thread_id = thread_id + "_and_"; 116 117 for( int i = 0; i < num_of_cameras; i++) 118 { 119 out.at(i).create(all_images.at(i).rows, all_images.at(i).cols, CV_8U); 120 cv::drawKeypoints(all_images.at(i), all_keypts[i], out[i], cv::Scalar(255,0,0)); 121 char no[20]; 122 sprintf(no,"Img:%d",i+1); 123 All_Images obj; 124 obj.image_title = thread_id + no; 125 obj.img = out[i]; 126 gl_images.push_back(obj); 127 } 128} 129 130int main(int argc, char** argv) 131{ 132 if(!ParseCommandLine(argc, argv)) 133 { 134 return 0; 135 } 136 137 const int num_images = FLAGS_images; 138 const int num_of_threads = FLAGS_threads; 139 const int num_of_iter = FLAGS_iterations; 140 std::string image_path = FLAGS_image_path; 141 142 std::vector<std::thread> threads; 143 144 for (int i = 0; i < num_of_threads; ++i) 145 { 146 std::string thread_name = "Thread:" + std::to_string(i + 1); 147 threads.emplace_back(extract, num_images, image_path.c_str(), thread_name, num_of_iter); 148 } 149 for (auto& thread : threads) 150 thread.join(); 151 152 //show the images 153 for (int i = 0; i < (num_images * num_of_threads); i++) 154 { 155 cv::imshow(gl_images[i].image_title, gl_images[i].img); 156 } 157 cv::waitKey(0); 158 159 return 0; 160}
Build the code:
Run the binary:
./feature_extract -h Following are the command line arguments: Usage: ./feature_extract --images=<> --image_path=<> --threads=<> --images <integer> : Number of images or number of cameras. Default value: 1 --image_path <string> : Path to input image files. Default value: image.jpg --threads <integer> : Number of threads to run. Default value: 1 --iterations <integer> : Number of iterations to run. Default value: 10 The following command, it will run four threads, each thread is taking two cameras image input. ./feature_extract --images=2 --threads=4
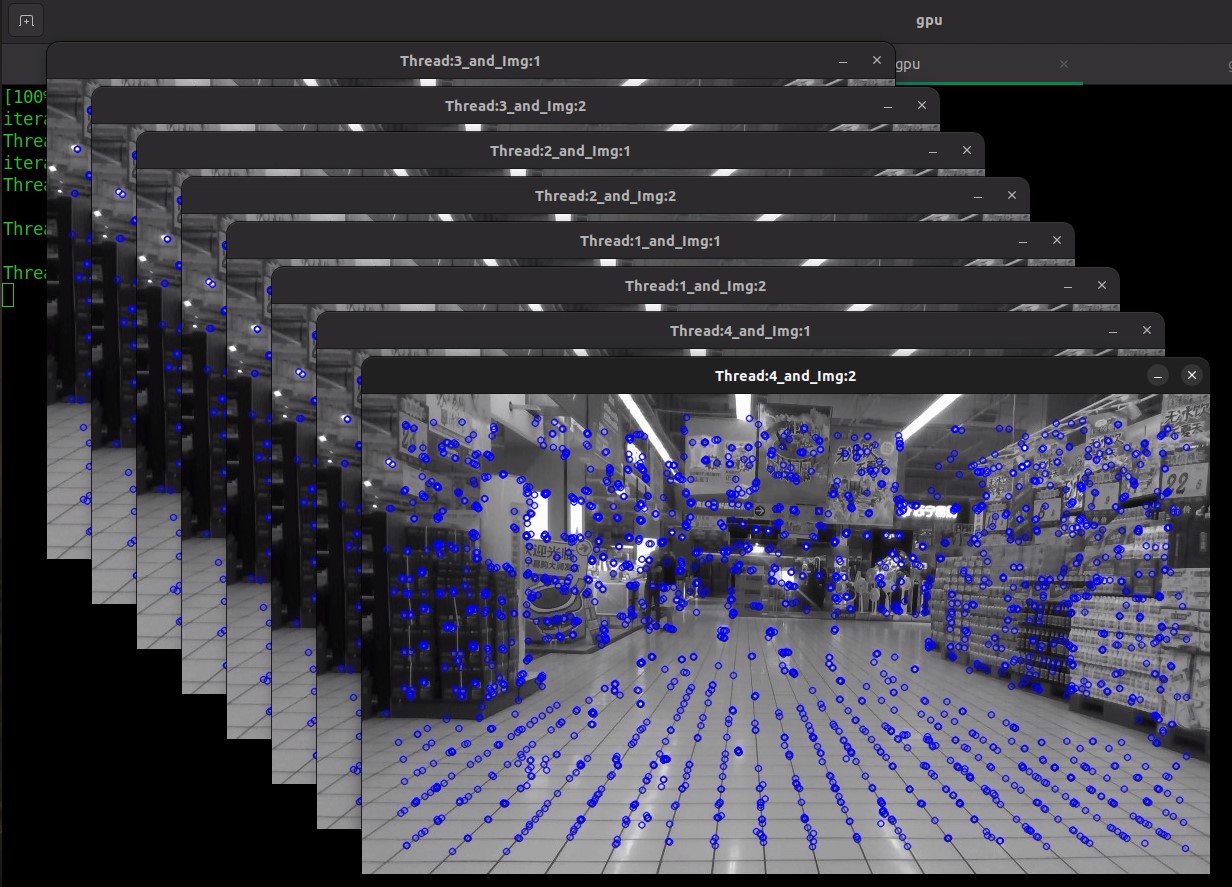
Expected results example:
After executing, the input image will display keypoints in blue color dots.
Note
Here, you can specify the number of images per thread and the number of threads to be executed. You have the option to process multiple image inputs within a single thread of the extract API or to process a single or more images input using multiple threads with extract API calls.
Code Explanation¶
Configuration for the ORB extractor:
Initialize the input and output parameters:
std::vector<cv::Mat> all_images;
all_images.resize(num_of_cameras);
for(int i = 0; i < num_of_cameras; i++)
{
all_images[i] = cv::imread(image_path, cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
}
std::vector<std::vector<KeyType>> keypts(num_of_cameras);
std::vector<MatType> all_descriptors(num_of_cameras);
#ifdef OPENCV_FREE
Mat2d *images = new Mat2d[num_of_cameras];
std::vector<MatType> in_image_array;
for( int i = 0; i < num_of_cameras; i++)
{
images[i] = Mat2d(all_images[i].rows, all_images[i].cols, all_images[i].data);
in_image_array.push_back(images[i]);
}
std::vector<MatType> in_image_mask_array;
std::vector<MatType> descriptor_array;
#else
const cv::_InputArray in_image_array(all_images);
const cv::_InputArray in_image_mask_array;
const cv::_OutputArray descriptor_array(all_descriptors);
#endif
Create orb_extract object:
Set gpu kernel path: Specify the path to GPU binaries such as gaussian_genx.bin, resize_genx.bin.
Note
The macro ORBLZE_KERNEL_PATH_STRING is defined as “/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu” in the header file config.h.
This header file is installed by the Deb package liborb-lze-dev at /usr/include/config.h.
Call the extract function to output the keypoints and descriptors for all camera input images. Depending on the number of camera inputs, the orb-extractor feature library returns the number of the keypoints vector and the descriptors vector.
Draw the keypoints on the image. Keypoints are drawn on the image and stored in respective CV:Mat vector.
std::vector<cv::Mat> out;
out.resize(num_of_cameras);
thread_id = thread_id + "_and_";
for( int i = 0; i < num_of_cameras; i++)
{
out.at(i).create(all_images.at(i).rows, all_images.at(i).cols, CV_8U);
cv::drawKeypoints(all_images.at(i), all_keypts[i], out[i], cv::Scalar(255,0,0));
char no[20];
sprintf(no,"Img:%d",i+1);
All_Images obj;
obj.image_title = thread_id + no;
obj.img = out[i];
gl_images.push_back(obj);
}
Create multiple threads. Each thread will create one orb-extractor feature object.
Display images: